DPM Replica Recovery Point Run Out of Space
If you receive an alert in System Center Data Protection Manager (DPM) that a replica or recovery point volume has run out of space, you will probably find this is a result of your DPM Storage Pool being out of space and head off to talk to your storage administrator to get some additional disk presented. While this is obviously the correct thing to do, you also need to take into consideration the impact this may have on your Recovery Point and Replica volumes.
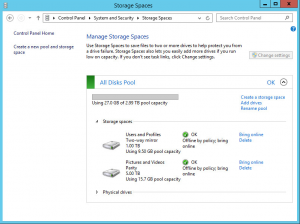
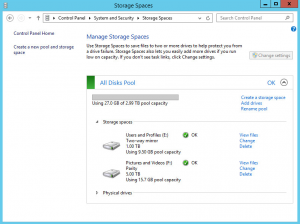
Once you have added a new disk to the server, you will add it to the DPM Storage Pool to extend the capacity of the pool. With the pool extended, it would be logical to assume that DPM will automatically extended the Replica and Recovery Point volumes and whilst this is true for normal operation that DPM will auto-grow these volumes if you have enabled the auto-grow feature, if you’re DPM Storage Pool completely filled before the new disk was added, you will need to do this manually. When DPM has attempted to auto-grow the partition on a previous attempt but been unable to do so due to insufficient disk space, it puts the Protection Group into a state where this operation is not attempted again automatically.
Imagine a scenario whereby a DPM server has a single 2TB volume in use for the Storage Pool. DPM creates many dynamic partitions on the disk to store your Protection Group data. When the disk fills and DPM needs to start using a new disk that you added, it will convert the existing dynamic partition into a spanned partition to allow it to span the multiple Storage Pool disks. If this operation occurs during normal DPM operation whereby there is sufficient free space to do so then it will happen automatically and you have nothing to worry about. If however, your DPM Storage Pool completely fills before it has a chance to convert it to a spanned partition, even once their capacity, DPM will stop trying to perform this operation.
Luckily for us, the fix is pretty simple. Locate the Protection Group which is reporting that the Replica or Recovery Point volumes are out of space and extend them manually using the DPM Central Console by any amount you like. It can be as little as 100MB if you need it to be. This manual extension will force DPM to read the data from the Windows Logical Disk Manager (LDM), it will see the new disk available and perform the span conversion operation.
If you can’t identify via the DPM Central Console which Protection Groups are faulting, another way is to look at the Disk Management console and look for partitions on the DPM Storage Pool disks which are not of type Spanned. Non-spanned partitions in this instance will be partitions which have not been pulled across both disks. This could be because that Protection Group hasn’t yet needed to be extended to make use of the new disk or it could be because it’s out of space but it’s a step in the right direct.
If you are extending the existing DPM Storage Pool disk instead of adding a new disk, I’m not exactly sure what would happen. If I had to hazard a guess, I would probably say that DPM will know about this uplift in capacity and extend the Protection Groups automatically as you are still working with the same disk, therefore no span conversion operation is required however I could be wrong? This is something for me to test in my new lab once I get it built.